|
|
|
|
|
foar 基于风热环境优化的多尺度城市设计——以苏州科技城核心区为例 |
|
|
论文标题:
期刊:
作者:hua liu, xin zhou, xin ge, dongqing han, weiren zhuang, ying tang, xiaohan shen
发表时间:august 2024
doi:
微信链接:
foar是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 a&hci / cscd / scopus / doaj / cstpcd 收录
01
论 文 题 目
manuscript title
multiscale urban design based on the optimization of the wind and thermal environments: a case study of the core area of suzhou science and technology city
基于风热环境优化的多尺度城市设计——以苏州科技城核心区为例
02
作 者
authors
hua liu (a)*, xin zhou (b), xin ge (a), dongqing han (b), weiren zhuang (a), ying tang (a), xiaohan shen (b)
(a) architects & engineers co., ltd of southeast university, nanjing 210096, china
(b) school of architecture, southeast university, nanjing 210096, china
03
论 文 摘 要
abstract
new methods are need to coordinate the conflicting spatial demands through urban design research and strategies from the perspective of multi-scale urban climate analysis. to integrate wind-thermal environment with urban design, we propose three scale levels, namely the district-superblock, superblock-block, and block-building levels, and divide the urban design elements into voids and solids. thereafter, we establish a multiscale methodological framework in which the urban design contents are clarified by each scale, and the information transmitted between scales is obtained to ensure consistent value propositions
and strategic approaches. the microclimate shaping of the urban open space is transformed into guiding strategies and quantitative indicators of the spatial form of the solid space. information is transmitted between the scales through the windethermal indicators of windward side and the morphological indicators of solid space. subsequently, the methodology was applied to the project in the core area of suzhou science and technology city, and the findings preliminarily verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the methodology. this research influences urban climate studies and urban design practice in three ways: 1) improving understanding of the correlation between scales; 2) facilitating interaction between the two domains; and 3) providing tools for urban design practices.
本文以绿色低碳发展为导向,探索基于多尺度城市风热环境优化的城市设计研究和设计新方法。为了有效并体系化地将风热环境研究向规划和城市形态学转化,研究提出了地段-超级街区、超级街区-街区、街区-建筑三个尺度层级,并将城市设计元素分为实体和虚体。之后,本研究搭建了多尺度信息传递的风热环境研究与城市设计关联的方法架构,明确了各尺度关注的设计内容及风热环境分析指标,提炼了各尺度传递的关键信息,确保各尺度优化任务在价值取向与策略方法上的一致性与可传递性。在同尺度层级上,以城市开放空间的微气候塑造为媒介,形成风热环境研究与城市设计的协同互动,将风热环境优化要求传递至城市形态中虚体和实体空间要素的形态控制策略和量化指标。在跨尺度层级上,风热环境方面通过迎风面相关指标传递,收缩研究模拟范围,城市设计方面依托实体空间的形态指标传递,确保高尺度的风热环境优化目标在低尺度有效落实。在实证中,将基于风热环境优化的多尺度城市设计方法应用于苏州科技城核心区项目,验证了该方法的有效性和可行性。本研究对城市气候研究和城市设计实践的影响主要体现在三个方面:1)提高对尺度层级间关联性的认知;2)促进气候学与城市形态学两个领域的互动;3)为城市设计实践提供方法工具。
04
关 键 词
keywords
multiscale transmission / 多尺度传递
windethermal environment optimization / 风热环境优化
urban design strategy / 城市设计策略
urban form / 城市形态
05
章 节 标 题
sections title
1. introduction / 引言
1.1. background / 研究背景
1.2. previous research / 研究综述
1.2.1. scales and elements / 尺度与要素
1.2.2. multiscale correlation between the research on the windethermal environment and the urban form / 风热环境与城市形态研究的多尺度关联
1.2.3. conclusions / 结论
1.3. objectives / 研究目标
2. methodology / 研究方法
2.1. defining the three scales / 对三个等级的定义
2.2. methodological framework / 方法论体系
2.3. scale 1: district-superblock / 层级1:区域-超级街区
2.3.1. basic model generation / 模型搭建
2.3.2. wind field and heat-island analysis / 风域与热岛分析
2.3.3. optimization of the open space structure and superblock model / 开放空间结构和超级街区模型优化
2.3.4. verification of the main and secondary wind corridor system / 主次风廊系统验核
2.3.5. transmitting superblock outlines / 层级信息传递
2.4. scale 2: superblock-block / 层级2:超级街区-街区
2.4.1. generation of the superblock-box model / 超级街区盒子模型搭建
2.4.2. installation of the ventilation corridors by season / 季节风廊分析
2.4.3. superposition and adjustment of multiseason wind corridors / 多季节风廊的叠加与验核
2.4.5. transmitting block morphology control content / 层级信息传递
2.5. scale 3: block-building / 层级3:街区-建筑
2.5.1. generation of the building-texture model / 建筑肌理模型搭建
2.5.2. inserting the open space / 开放空间置入
2.5.3. optimizing the interfaces / 优化界面
2.5.4. verification of the building-texture model / 建筑肌理验核
2.6. case study / 案例研究
3. results and analysis / 研究成果与分析
3.1. scale 1: district-superblock / 层级1:区域-超级街区
3.2. scale 2: superblock-block / 层级2:超级街区-街区
3.3. scale 3: block-building / 层级3:街区-建筑
4. discussion and conclusion / 讨论与结论
06
主 要 插 图
illustrations
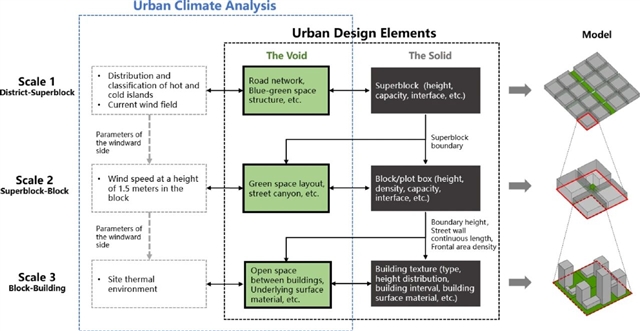
▲ 图一:研究框架展示了城市气候与城市设计的研究对象、各尺度研究与设计内容、多尺度信息传递之间的关系。© 本文作者
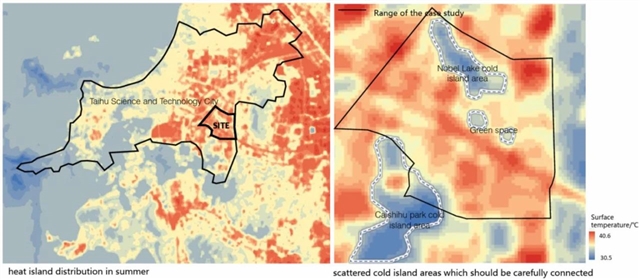
▲ 图二:热环境模拟及现场分析。© 本文作者
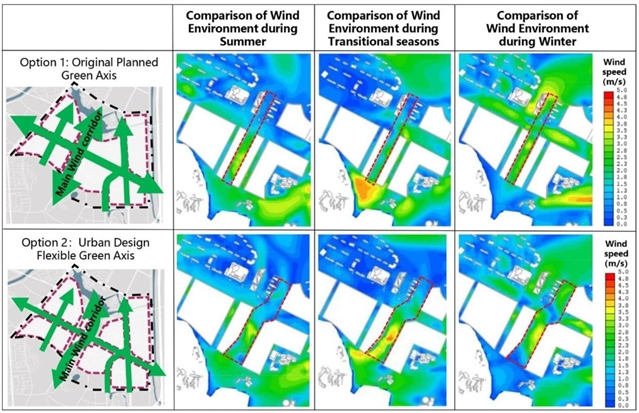
▲ 图三:优化方案与原规划方案开放空间风环境性能比较。© 本文作者
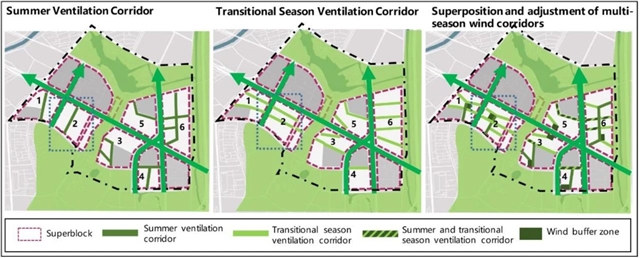
▲ 图四:通风廊道的设置、叠加和优化。© 本文作者
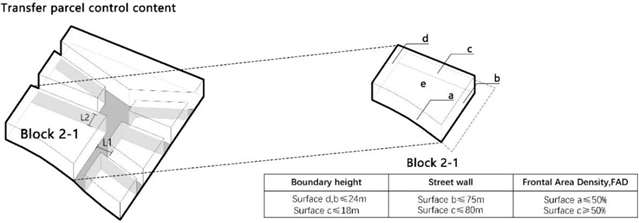
▲ 图五:以block2-1的形态管控信息传递为例。© 本文作者
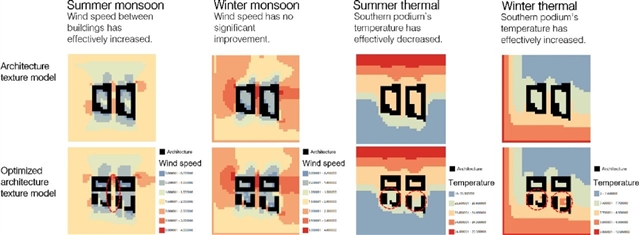
▲ 图六:对风、热环境进行模拟,并对优化前后的建筑肌理模型进行对比。© 本文作者
07
作 者 介 绍
authors’ information

刘 华
东南大学建筑设计研究院有限公司执行总规划师
兼任东南大学建筑学院硕导
当前研究方向:多学科互动关联下的城市设计方法、绿色低碳导向下的多尺度城市设计技术方法、高质量发展导向下的精细化城市设计与管控方法等。

周 欣
东南大学建筑学院 副教授、博士生导师
东南大学建筑学院建筑技术与科学研究所副所长
当前研究方向:低碳城市建筑环境、柔性负荷预测与分析、绿色建筑、绿色低碳建筑性能仿真、建筑节能技术、建筑能源需求特征分析、人员能耗行为仿真。

葛 欣
东南大学建筑设计研究院有限公司 建筑师
研究方向:集约化城市形态及其设计
韩冬青
全国工程勘察设计大师
东南大学建筑学院教授、博士生导师
东南大学建筑设计研究院有限公司首席总建筑师
当前研究方向:城市建筑学;城市更新;建筑设计及其理论

庄惟仁
东南大学建筑设计研究院有限公司 助理建筑师
当前研究方向:绿色城市设计、绿色建筑设计

唐 滢
东南大学建筑设计研究院有限公司 建筑师
当前研究方向:绿色城市设计

沈晓寒
东南大学建筑学院 博士
当前研究方向:城市微气候、城市通风性能、绿色低碳建筑性能模拟、机器学习
08
原 文 阅 读
download link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
▼ 点击下方词条 | 往期精彩不容错过
#期刊快讯#系列
#新刊上线#系列
#foar投稿指南#系列
#期刊知识科普#系列
#精彩文章#系列精选
期刊联络
高等教育出版社: 010-58556484
东南大学:025-83795543
刊物邮箱:foar@pub.seu.edu.cn
foar英文期刊交流qq群:21608832
在线投稿
刊物yabo亚博88主页
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被sci收录,其他也被a&hci、ei、medline或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负yabo亚博88的版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。