|
|
|
|
|
foar 基于bim和机器学习的基础物化阶段碳排放预测——以中国35座公共建筑为例 |
|
|
论文标题:
期刊:
作者:haining wang , yue wang ,liang zhao,wei wang, zhixing luo, zixiao wang , jinghui luo, yihan lv
发表时间: august 2024
doi:
微信链接:

foar是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 a&hci / cscd / scopus / doaj / cstpcd 收录

01
论 文 题 目
manuscript title
integrating bim and machine learning to predict carbon emissions under foundation materialization stage: case study of chinas 35 public buildings
基于bim和机器学习的基础物化阶段碳排放预测——以中国35座公共建筑为例
02
作 者
authors
haining wang (a)(b), yue wang (c)(d), liang zhao (e), wei wang (a)*,zhixing luo (b)(f)**, zixiao wang (a), jinghui luo (e), yihan lv (a)
(a) school of architecture, southeast university, nanjing 210096, china
(b) key laboratory of urban and architectural heritage conservation (southeast university), ministry of education, nanjing 210096, china
(c) school of architecture, xian university of architecture and technology, xian 710055, china
(d) hubei haizheng technology co., ltd, wuhan 430000, china
(e) school of energy and environment engineering, hebei university of engineering, handan 056038,
china
(f) state key laboratory of green building, xi’an university of architecture and technology, xian
710055, china
03
论 文 摘 要
abstract
for the significant energy consumption and environmental impact, it is crucial to identify the carbon emission characteristics of building foundations construction during the design phase. this study would like to establish a process-based carbon evaluating model, by adopting building information modeling (bim), and calculated the materialization-stage carbon emissions of building foundations without basement space in china, and identifying factors influencing the emissions through correlation analysis. these five factors include the building function type, building structure type, foundation area, foundation treatment method, and foundation depth. additionally, this study develops several machine learning-based predictive models, including decision tree, random forest, xgboost, and neural network. among these models, xgboost demonstrates a relatively higher degree of accuracy and minimal errors, can achieve the rmse of 206.62 and r² of 0.88 based on testing group feedback. the study reveals a substantial variability carbon emissions per buildings floor area of foundations, ranging from 100 to 2000 kgco?e/㎡, demonstrating the potential for optimizing carbon emissions during the design phase of buildings. besides, materials contribute significantly to total carbon emissions, accounting for 78%-97%, suggesting a significant opportunity for using bim technology in the design phase to optimize carbon reduction efforts.
建筑基础施工对能源消耗和环境影响较大,在设计阶段确定其碳排放特征至关重要。本研究拟建立基于过程的碳排放评价模型,采用建筑信息模型(bim),计算中国不含地下室空间的建筑基础物化阶段的碳排放量,并通过相关分析找出影响排放的因素。这五个因素包括:建筑功能类型、建筑结构类型、基础面积、基础处理方法、基础深度。此外,本研究还开发了几种基于机器学习的预测模型,包括决策树、随机森林、xgboost和神经网络。在这些模型中,xgboost具有较高的精度和最小的误差,根据测试组的反馈,可以实现rmse为206.62, r² 为0.88。该研究揭示了每个建筑物的基础建筑面积的碳排放量的巨大变化,范围从100到2000 kgco?e/㎡,显示了在建筑设计阶段优化碳排放的潜力。此外,材料对总碳排放量的贡献很大,占78%-97%,这表明在设计阶段使用bim技术优化碳减排工作的机会很大。
04
关 键 词
keywords
building foundations / 建筑基础
carbon emissions / 碳排放
building information modeling / 建筑信息模型
machine learning / 机器学习
sustainable architectural design / 可持续建筑设计
05
章 节 标 题
sections title
1. introduction / 引言
2. literature review / 文献综述
3. methodology / 研究方法
3.1. system boundary / 系统边界
3.2. functional unit / 功能单元
3.3. quantitative approach / 定量方法
3.4. models used for calculating emissions / 用于计算排放量的模型
3.5. extracting factors affecting from bim model / 从bim模型中提取影响因素
3.6. predictive model used for calculating carbon emissions / 用于计算碳排放量的预测模型
3.6.1. evaluation index / 评价指标
3.6.2. data preprocessing / 数据预处理
3.6.3. machine learning algorithm deployment / 机器学习算法部署
4. case study / 案例研究
5. results and discussion / 研究成果及讨论
5.1. results of carbon emission / 碳排放的结果
5.2. comparison with other cases / 与其他案例进行对比
5.3. correlation factor analysis / 相关因素分析
5.4. predictive model building / 建立预测模型
5.5. sensitivity analysis / 敏感性分析
5.6. limitation and future works / 局限性及未来的工作
6. conclusion / 结论
06
主 要 插 图
illustrations
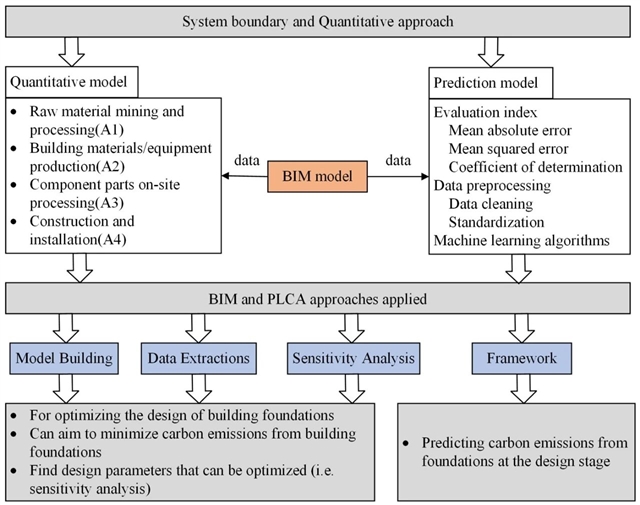
▲ 图一:地基基础物化阶段碳排放量计算框架。© 本文作者
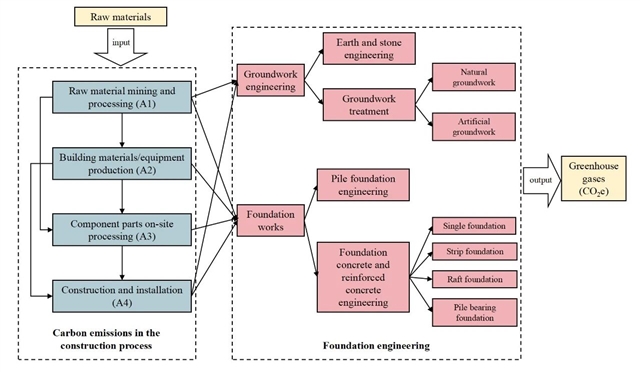
▲ 图二:地基基础与建筑物化碳排放的逻辑关系。© 本文作者
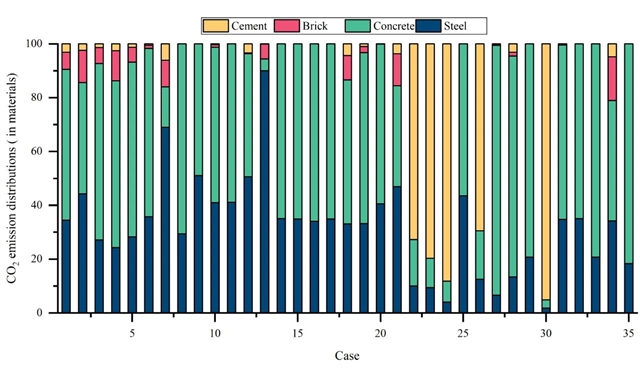
▲ 图三:案例地基基础材料碳排放占比分析。© 本文作者
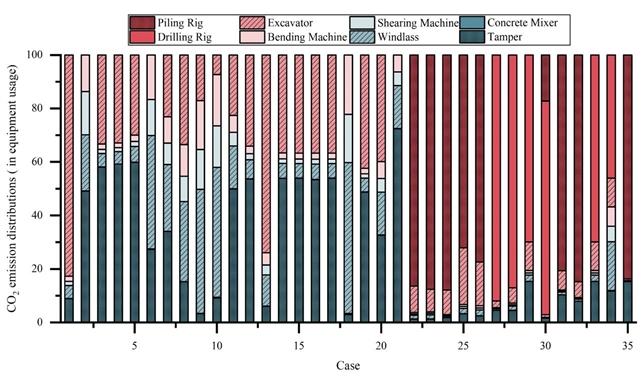
▲ 图四:案例地基基础机械设备碳排放占比分析。© 本文作者
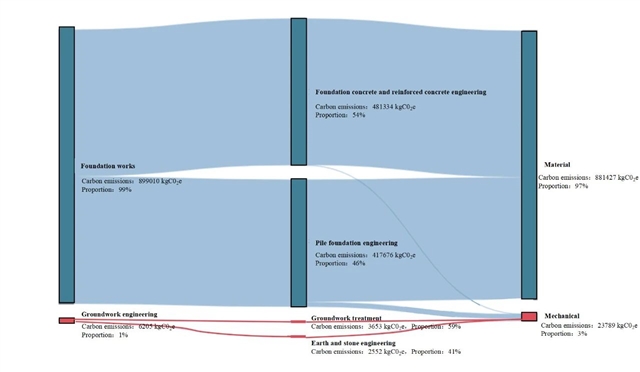
▲ 图五:地基基础物化阶段碳排放路径。© 本文作者
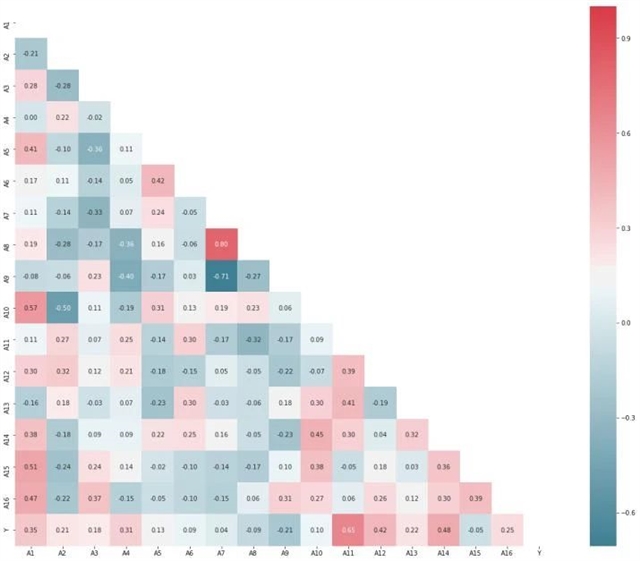
▲ 图六:地基基础物化碳排放影响因素相关性热点图。© 本文作者
07
作 者 介 绍
authors’ information

王海宁
讲师
东南大学建筑学院
主要专业方向:装配式建筑、建筑碳排放、bim、标准化建筑设计、方案设计定量优化。

王 玥
绿色建筑咨询工程师
中创汇科(武汉)科技有限公司
西安建筑科技大学硕士毕业。主要研究方向:绿色建筑设计、建筑碳排放、能碳数字平台。

赵 亮
讲师
河北工程大学能源与环境工程学院
主要研究方向:建筑碳排放,bim,机器学习。

王 伟
副研究员
东南大学建筑学院
东南大学a类至善学者,东南大学五四青年奖章获得者,江苏省双创人才,入选第三批全国高校黄大年式教师团队。主要研究方向绿色城市设计、极端气候与基础设施环境设计。

罗智星
教授
西安建筑科技大学
入选国家级人才青年项目。主要研究方向为绿色低碳建筑设计方法与技术。

王子骁
本科在读
东南大学建筑学院
主要研究方向:建筑碳排放、机器学习。
罗景辉
讲师、空调制冷系主任
河北工程大学
主要研究方向:地热能开发利用、低品位热能回收利用、热泵理论与应用、区域能源规划等领域的研究工作。

吕依涵
硕士
中建海龙科技有限公司
东南大学建筑学硕士,现工作于中建海龙科技有限公司。主要研究方向:装配式建筑、bim、数字孪生。
08
原 文 阅 读
download link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
▼ 点击下方词条 | 往期精彩不容错过
#期刊快讯#系列
#新刊上线#系列
#foar投稿指南#系列
#期刊知识科普#系列
#精彩文章#系列精选
期刊联络
高等教育出版社: 010-58556484
东南大学:025-83795543
刊物邮箱:foar@pub.seu.edu.cn
foar英文期刊交流qq群:21608832
在线投稿
刊物yabo亚博88主页
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被sci收录,其他也被a&hci、ei、medline或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负yabo亚博88的版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。