|
|
|
|
|
foar 喷雾系统对中国西安市半户外空间下席坐人们热环境和热舒适性的影响 |
|
|
论文标题:
期刊:
作者:xu xie, zhen sun, xi zhu, shengkai zhao, zun wang, yongchao zhai
发表时间:june 2024
doi:
微信链接:

foar是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 a&hci / cscd / scopus / doaj / cstpcd 收录

01 论 文 题 目 manuscript title
influence of misting system on the thermal environment and thermal comfort of seated people in semi-outdoor space in xian, china
喷雾系统对中国西安市半户外空间下席坐人们热环境和热舒适性的影响
02 作 者 authors
xu xie (a), zhen sun (a)(b), xi zhu (a)(b), shengkai zhao (a)(b), zun wang (a)(b), yongchao zhai (a)(b)*
(a) college of architecture, xian university of architecture and technology, xian 710055, china
(b) state key laboratory of green building, xian university of architecture and technology, xian 710055, china
03 论 文 摘 要 abstract
in summer, factors such as solar radiation could make semi-outdoor spaces uncomfortable, and the use of misting systems for evaporative cooling is a low-energy improvement measure. to investigate the impact of misting system on the thermal environment and thermal comfort of seated people improvement, a field study was conducted at a semi-outdoor cafeteria in xian. the results indicated that the misting system was capable of reducing the ambient air temperature by 2.4-4.9℃and increasing the relative humidity by 17.1%-17.8%. participants in misting condition reported lower thermal sensation and higher thermal acceptability, thermal preference, humidity sensation, humidity preference and humidity acceptability. in no misting condition, the upper set* limit acceptable to 80% of the population was 28.5℃. however, in the misting condition, the acceptable percentage of participants in each set* interval was more than 90%. when set* was 22.1-23.7℃, the improvement in human thermal comfort through misting system was not significant. when set) was 23.7-28.5 ℃, the misting system significantly improve human thermal comfort. finally, two control temperature thresholds of the misting system were provided according to the relationship between 80%, the maximum (89.3%) acceptable percentage and the air temperature, which were 30.1℃ and 26.5℃, respectively.
在夏季,太阳辐射等因素可能使半户外空间变得不舒适,而雾化系统作为一种低能耗的改进措施,可以用于蒸发冷却。为了研究雾化系统对半户外环境下席坐人们的热舒适度的影响,在西安的一家半户外餐厅进行了实地研究。结果表明,雾化系统能够将环境空气温度降低2.4-4.9℃,并将相对湿度提高17.1%-17.8%。在雾化条件下,参与者报告的热感觉较低,同时热接受度、热偏好、湿度感觉、湿度偏好和湿度接受度均较高。在没有雾化的情况下,80%的人群能够接受的最高set限值为28.5℃。然而,在雾化条件下,各set区间内的参与者接受百分比均超过90%。当set在22.1-23.7℃时,雾化系统对人类热舒适度的改善不显著;而当set在23.7-28.5℃时,雾化系统显著改善了人类热舒适度。最后,根据80%、最大可接受百分比(89.3%)与空气温度之间的关系,提供了两个雾化系统的控制温度阈值,分别为30.1℃和26.5℃。
04 关 键 词 keywords
misting system / 喷雾系统
thermal environment / 热环境
thermal response / 热响应
acceptable temperature / 可接受温度
control strategy / 控制策略
05 章 节 标 题 sections title
1. introduction / 引言
2. methodology / 研究方法
2.1. location and climate / 区位与气候
2.2. building and respondents / 建筑与响应
2.3. field investigations procedure / 实地调查过程
2.3.1. physical parameters measurements / 物理参数测量
2.3.2. subjective questionnaires / 主观问卷调查
2.4. statistical analysis / 统计分析
3. results / 研究结果
3.1. thermal environments / 热环境
3.2. factors of influencing thermal comfort / 影响热舒适的因素
3.3. subjective responses / 主观反应
3.4. neutral temperature and acceptable temperature / 中性温度和可接受温度
4. discussion / 讨论
4.1. effective temperature range for thermal comfort improvement by misting system / 喷雾系统提高热舒适性的有效温度范围
4.2. control strategy for misting system in semi-outdoor space / 半户外空间喷雾系统的控制策略
4.3. limitations of this study / 本研究的局限性
5. conclusion / 结论
06 主 要 插 图 illustrations
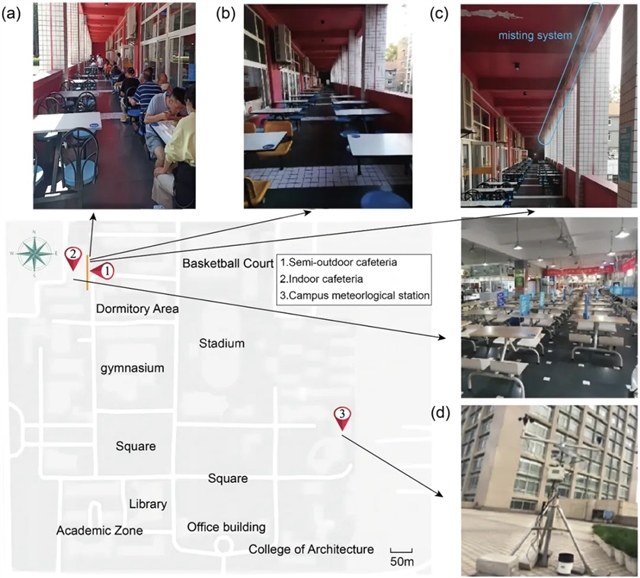
▲ 图一:对建筑位置和场景的调查。(a) 一楼食堂(无喷雾系统);(b) 二楼食堂(无喷雾系统);(c) 二楼食堂(有喷雾系统);(d) 校园气象站。© 本文作者
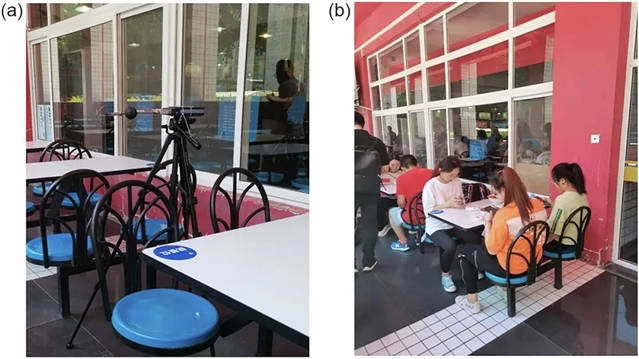
▲ 图二:实地调查场景。(a) 物理环境参数测试;(b) 主观问卷调查。© 本文作者
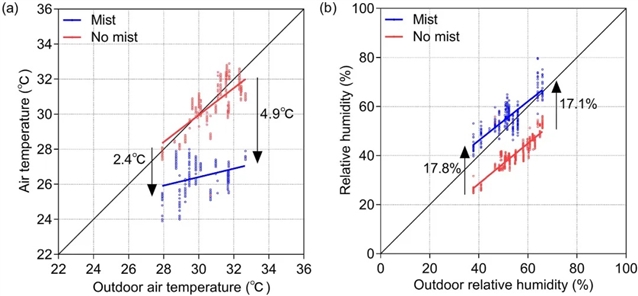
▲ 图三:喷雾系统的存在或缺失对物理环境的影响。(a) 气温变化;(b) 相对湿度变化。© 本文作者
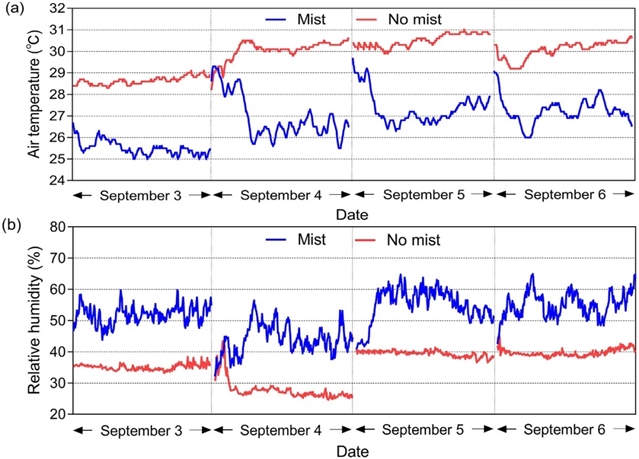
▲ 图四:喷雾系统有无情况下物理环境随时间的变化。(a) 气温变化;(b) 相对湿度变化。© 本文作者
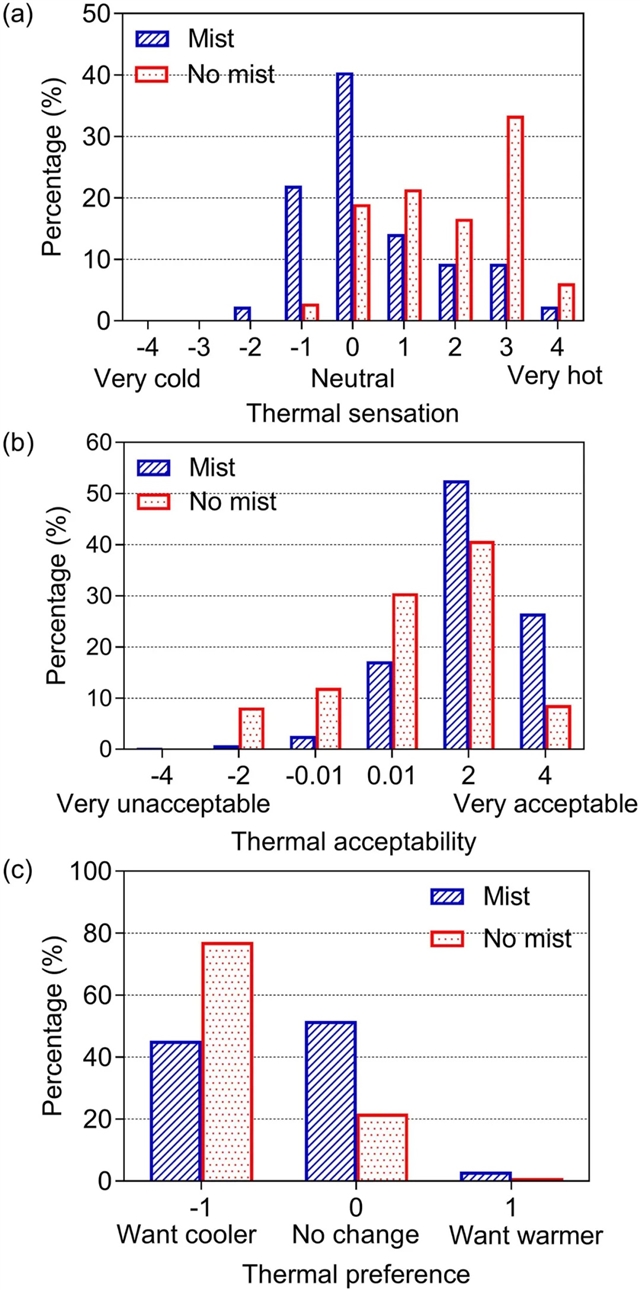
▲ 图五:热反应的分布情况。(a) 热感觉投票的分布;(b) 热可接受性投票的分布;(c) 热偏好投票的分布。© 本文作者
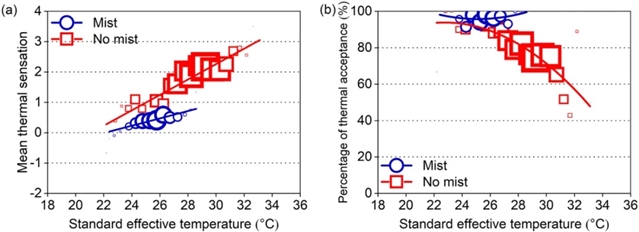
▲ 图六:中性温度和可接受温度。(a) 平均热感觉与标准有效温度的关系;(b) 热接受度与标准有效温度的关系。© 本文作者
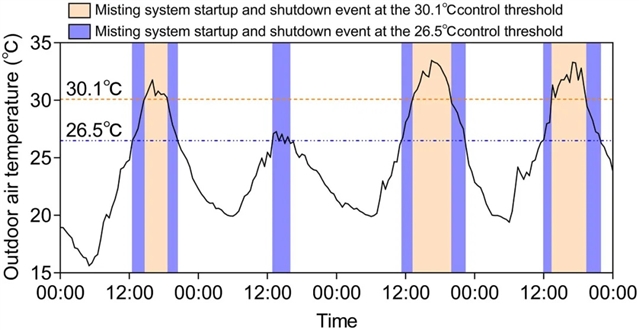
▲ 图七:半户外空间喷雾系统的控制策略。© 本文作者
07 作 者 介 绍 authors’ information

谢旭
在读博士研究生
西安建筑科技大学 建筑学专业
主要研究方向:大型公共交通建筑、建筑热环境。

孙震
在读博士研究生
西安建筑科技大学 建筑学专业
主要研究方向:建筑热环境、人体热舒适与热适应。

朱曦
在读博士研究生
西安建筑科技大学 建筑学专业
主要研究方向:建筑热环境、人体热舒适、建筑声环境。

赵胜凯
讲师
河南理工大学 建筑与艺术设计学院
2024年获西安建筑科技大学建筑学博士学位。主要研究方向为建筑热环境、人体热舒适与热适应。

王尊
硕士
西安建筑科技大学 建筑学专业
主要研究方向:建筑热环境与人体热舒适。

翟永超
教授 / 博导
西安建筑科技大学 建筑学院
2013年获华南理工大学博士学位,先后在加州大学伯克利分校、西安建筑科技大学进行博士后研究,2016年入选陕西省“百人计划”青年项目。研究方向为人体热舒适和低能耗建筑室内热环境营造。主持国家自然科学基金3项,陕西省重点产业创新链项目1项,主持其它省部级纵向课题3项,作为研究骨干参与“十三五”重点研发项目1项。参编国家行业、团体和地方标准3项。近年来在国内外重要刊物发表研究论文30余篇,被引2100余次(google scholar)。任ashrae tc 2.1 research subcommittee chair,2021年获ashrae ralph nevins生理与人类环境奖。
08 原 文 阅 读 download link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
▼ 点击下方词条 | 往期精彩不容错过
#期刊快讯#系列
#新刊上线#系列
#foar投稿指南#系列
#期刊知识科普#系列
#精彩文章#系列精选
期刊联络
高等教育出版社: 010-58556484
东南大学:025-83795543
刊物邮箱:foar@pub.seu.edu.cn
foar英文期刊交流qq群:21608832
在线投稿
刊物yabo亚博88主页
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被sci收录,其他也被a&hci、ei、medline或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负yabo亚博88的版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。